Bringing Generative AI to Digital Twins: Matterport’s Three Pillars of AI
Generative AI has taken the world by storm. As each day introduces countless new applications applying the latest technology trends– from conversational AI, to text-to-image, text-to-video, and beyond– the research community is moving at breakneck speed to both understand, and build on, breakthroughs that will shape the future of everything we do.
More than a decade ago, Matterport made it easy for anyone to create a 3D digital twin for buildings and spaces. Our industry-first solution, Cortex AI, is powered by AI and fully automated, allowing us to create thousands of digital twins daily without human intervention. For Matterport, generative AI represents an opportunity for a step-function evolution of our digital twins, transforming what today reflects the current state of an environment, to in the future, reflect what an environment could become.
Generative AI promises the potential to dramatically improve the operating efficiency and decision-making process in the property sector. By combining Matterport’s valuable property insights with the ability to automatically enhance the design, layout, and utility of a property, our suite of AI real estate solutions will provide customers with more tools than ever to enhance their property’s value.
In this new blog series, we will dive into Matterport’s path to deliver generative AI to the built world.
We begin with our approach to AI at Matterport in the context of the company’s recently published research on generative AI.
Three Pillars of AI: Reconstruction, Understanding, and Synthesis
AI has been a part of our technical evolution for more than a decade, helping revolutionize 3D capture for the built world.
It began when we first made it easy for anyone to create 3D “digital twins”-- dimensionally-accurate replicas of 3D environments– for buildings and spaces, and has continued to grow with the introduction of solutions like Property Intelligence and Project Genesis– the company’s vision for generative AI in Matterport’s digital twin platform.
Today, you can think of Matterport’s approach to AI in three pillars: 1) Reconstructing 3D spaces, 2) understanding 3D data, and 3) synthesizing 3D data.
Reconstruction of 3D Spaces: Cortex AI
It all begins with capturing and reconstructing a space in digital 3D.
Matterport is powered by its proprietary Cortex AI - a deep learning neural network that combines computer vision, advanced image processing, and deep learning to fully automate the 3D reconstruction of any physical space captured.
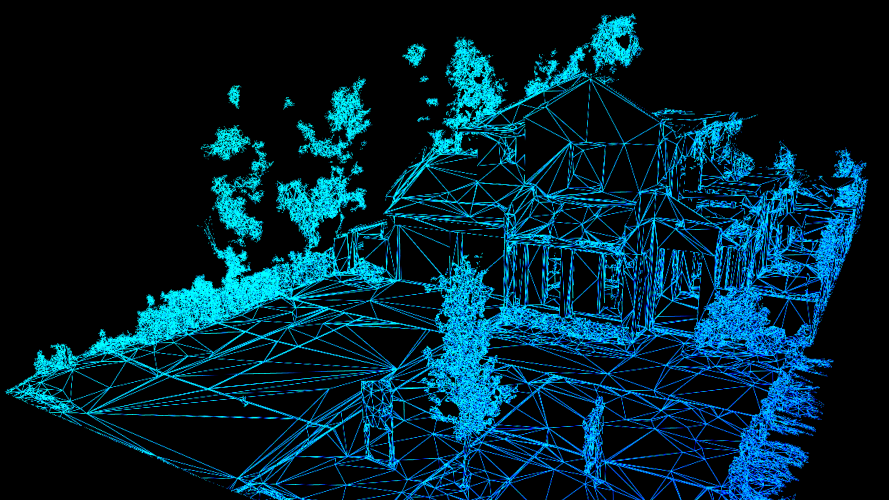
Cortex represented a major milestone for the 3D capture industry as the first fully automated solution that scales effortlessly in terms of square footage captured, time to scan, and cost to produce.
This has driven the rapid global adoption of Matterport digital twins, enabling anyone to easily replicate a place in 3D, whether with the latest state-of-the-art cameras, or the smartphone in your pocket.
Understanding 3D Data: Property Intelligence
Fast-forward more than a decade, and Cortex has enabled the digitization of 12+ million spaces, representing more than 38 billion square feet of space– or roughly twice the size of the cities of New York and Los Angeles combined.
With a wealth of data representing every type of building environment – from homes, to construction, industrial facilities and beyond – our teams focused on creating data structures that capture and surface this information to customers in the form of automated insights that were previously unattainable for properties at this scale.
To do this, Matterport’s team had to solve how to transform raw data from numbers, geometry and color captured in the billions of pixels that make up a Matterport scan.
For example, when a person walks into a home and sees a sofa, coffee table, and a TV in an open space, they will quickly recognize that this is a living room – whereas if they see a single desk with a chair, this could be an office. Building this level of understanding in a computer is significantly more complex, requiring it to learn semantic rules for what each square centimeter, color and physical space means, trained on vast amounts of data.
Matterport’s Property Intelligence is fundamentally changing how property data is collected and reported, from automatically calculating the square footage of a space scanned or the ceiling height, or identifying common rooms and areas based on the objects it sees in a space.
But the data it captures goes well beyond this, identifying information like, lighting, ventilation, plumbing, and more.
The datafication of built environments is laying the foundation for the next decade of advancements in property insights, enabling property stakeholders of all kinds – from buyers, sellers, and agents, to designers, builders and property managers – to maximize the value of any space.
Synthesizing 3D Data: Bringing Generative AI to Matterport
With the largest spatial data library in the world, Matterport has a trove of property data organized, labeled and understood, and the next evolution will be enabling Matterport models to synthesize new information that allow for the modification and extension of Matterport’s digital twins with generative AI.
While 3D digital twins excel in replicating existing conditions with remarkable accuracy, they have historically lacked the flexibility to adapt to different downstream scenarios and requirements without significant manual effort. By layering generative technology onto Matterport’s spatial data platform, this barrier is removed and the future promises nearly limitless possibilities stemming from a single digital twin.
The ability to dynamically make changes with ease, such as automatically reimagining and redesigning a space within the digital twin, will offer powerful benefits that create more value for our customers.
Homeowners, designers, and property managers reimaging a physical space using generative AI for interior design and staging, while architects and facility managers get the automation tools that helps them create more efficient, sustainable, and accessible buildings.
In research published today by Matterport’s Vision & Learning team, the team demonstrated its latest advancements with generative AI implemented in Matterport twins, utilizing the latest in open source research and cutting edge technologies like Stable Diffusion to propose a novel approach to removing furniture or objects from the panoramic images in a digital twin.
Matterport Introduces Novel Approach to Defurnishing
Advancements in Stable Diffusion, a popular deep learning, text-to-image model, have increased rapidly in the past year, unlocking new opportunities for generative-based visual technologies.
A common technique used in Stable Diffusion is inpainting. Made popular by generative AI models like Dall-E, inpainting involves analyzing existing visual cues within an image to intelligently fill in missing or damaged areas, such as expanding the boundaries of a photo, or reimagining it in a famous artist's style.
Recognizing the potential to apply inpainting to a Matterport model, Matterport’s machine learning team began exploring a new solution leveraging the open source tools and the latest research to automatically defurnish a Matterport model.
Looking Ahead
Solving problems in 3D is highly complex, and we’re still in the early stages of what the latest in technology can accomplish.
As we make progress on our generative AI initiatives, we’ll be sharing regular updates with the community about the problems we’re solving, and the solutions we’ve implemented on our path to deliver a future of generative AI enhancements to our digital twin platform.
Read our research paper on the topic, and stay tuned to this blog for future insights into our research and the journey toward bringing generative AI to the built world in novel ways that help our customers unlock new opportunities to save time, save money, and increase productivity.

