Digital Transformation In Manufacturing: Benefits & How To Adapt
Benefits & Inspiration To Get Started
Manufacturing is evolving faster than at any point in history. The kind of innovation that used to take 100 years? Now it's happening in just a decade.
Industry 4.0 introduced AI, robotics, IoT, and digital twins, to create smart ecosystems that fundamentally changed how factories operate. Now Industry 5.0 is slowly emerging, shifting the focus back to human creativity, sustainability, and resilience.
While the opportunities in manufacturing are enormous, leaders are feeling the heat of rapid change. This guide explores how to balance big investments in technology and, at the same time, take small steps that deliver meaningful results today.
What is digital transformation in manufacturing?
Digital transformation in manufacturing builds on the idea of automation and intelligent factories. Digital transformation isn't just about automation and smart factories anymore.
From the 1970s to the 2000s, automation was the hallmark of Industry 3.0. It replaced manual labor with programmable logic controllers and basic robotics.
We've now progressed to Industry 4.0, where factories and products can essentially optimize themselves. The webinar below shows how AI, Industrial Internet of Things (IIOT), and big data work together to transform manufacturing.
Industry 5.0 is starting to emerge as AI tools grow smarter. With many tasks now automated, the focus shifts to empowering workers to achieve greater effectiveness.
The table below explains the different categories of digital transformation that you can adopt to increase efficiency and competitiveness.
Category | Data & Tools Required | Impact on Manufacturing |
Industrial IoT (IIoT) | Sensors, connected devices, SCADA data | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, reduced downtime |
Artificial intelligence (AI) | Machine learning models, analytics platforms | Smarter decision-making, defect detection, demand forecasting |
Predictive analytics | Historical + real-time machine data, big data lakes | Anticipates failures, optimizes maintenance schedules, boosts OEE |
Cloud computing | Centralized data storage, SaaS platforms | Remote access, scalability, enterprise-wide integration |
Big data | High-volume data from machines, ERP, MES | Improved forecasting, optimized inventory, supply chain transparency |
Automation & robotics | PLCs, cobots, robotic arms, automated material handling | Higher throughput, lower errors, safer working conditions |
Digital twins | 3D scans, IoT integration, simulation tools | Virtual prototyping, immersive training, sustainability planning |
Cybersecurity | Secure networks, access controls, compliance frameworks | Protects IP, ensures compliance, builds trust in digital systems |
6 key benefits of digital transformation in manufacturing
Over the next decade, we're looking at reinvention that could rival the assembly line itself. Here’s how digital transformation is helping manufacturers slash costs, beef up their supply chains, and streamline operations across the board.
1. Improved production process efficiency
Digital transformation raises both product quality and output, reducing inefficiencies and making an immediate impact on profits.
In many factories, the intended process and the real process diverge significantly. Digital transformation reduces this mismatch by giving leaders visibility into what’s really happening—and the tools to correct it in real time.
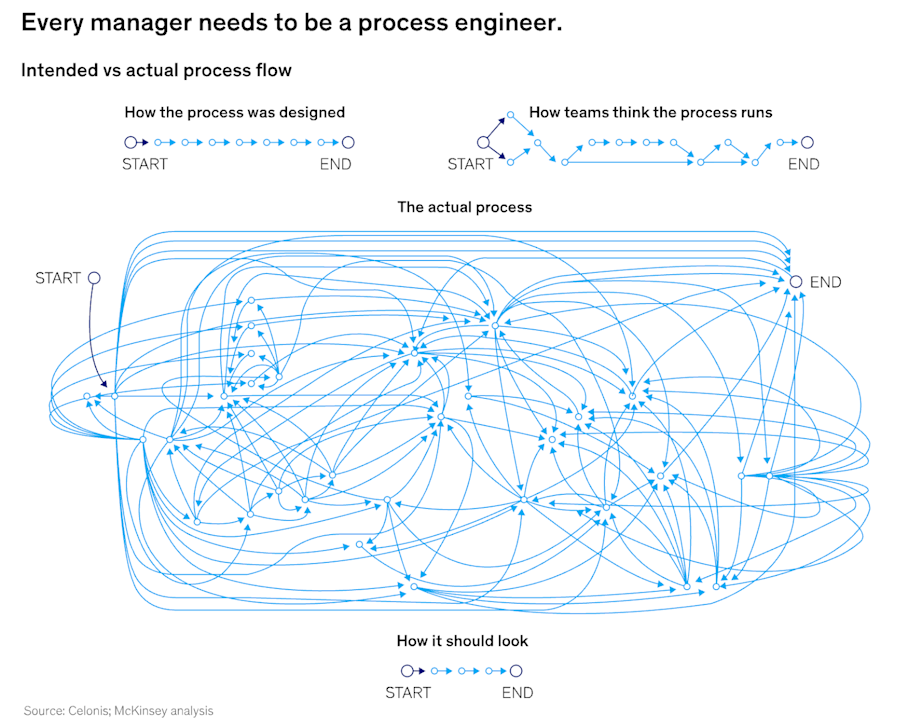
The real process is often different to how the process was originally intended to run. Digital transformation helps simplify processes for manufacturing facility managers. (Source)
Technology like digital twins turns factory floors into accurate virtual models that streamline operations across the board. Leaders gain real-time visibility into facility maintenance, inventory, and training—catching problems before they stop production.
2. More resilient supply chain and inventory transparency
Here's what the right technology actually lets you do:
Improve inventory management by automating tracking and supply routes
Forecast demand with greater accuracy using predictive models
Simulate supply scenarios so teams can predict and resolve bottlenecks
Instead of reacting to disruptions, manufacturers can increasingly predict problems and optimize operations.
3. Better cost efficiency for facility operations
Digital transformation tools and processes aim for cost optimization in almost every area of manufacturing:
Reducing wastage and hidden expenses
Optimizing facility space
Increasing mechanical outputs
Increasing human productivity
Optimizing maintenance and extending equipment life
Here's what many leaders don't realize: ignoring digital tools costs way more than adopting them. When you delay modernization, you risk losing market share as competitors move faster and deliver at a higher quality. Outdated equipment also drives up insurance premiums and leads to compliance fines.
On the flip side, digital investments typically deliver solid ROI. For example, productivity-focused transformation saves 50% more on costs compared to more traditional cuts like layoffs or reduced output.
4. Reduced downtime with predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance reduces downtime by spotting equipment issues in real-time, so you can fix them before they turn into expensive failures.
Reactive or scheduled maintenance waits for failure, but predictive maintenance uses AI, IIoT sensors, and real-time analytics to anticipate problems.
Where reactive maintenance falls short | How predictive maintenance excels |
A conveyor motor fails unexpectedly, halting a bottling line for a full shift. Emergency parts and overtime labor drive up costs. | IoT sensors detect abnormal vibration in the motor a week earlier. The part is ordered in advance, and a short planned service window avoids downtime. |
An HVAC system breaks down in midsummer, increasing energy costs and creating unsafe working conditions until repairs are made. | Smart sensors track efficiency drops in the HVAC system. Maintenance crews replace the failing component early, preventing disruption and safety risks. |
A critical pump seizes during production, causing product loss and a missed customer delivery. | Analytics flag pressure irregularities in the pump, prompting a quick repair during off-hours. Production continues on schedule with no lost output. |
Digital twin technology makes predictive maintenance even more practical by displaying IIoT sensor data on a realistic view of your factory floor.
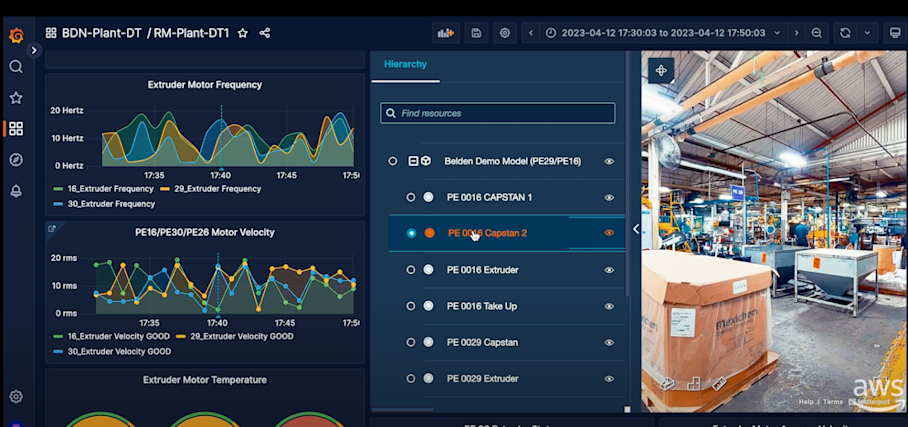
This dashboard shows IIoT sensors track extruder motor data points and overlay those onto a manufacturing facility’s digital twin (Source)
5. Safer workplaces
Digital transformation reduces human exposure to hazards by increasing the quality of remote audits and inspections—fewer people in harm's way.
Here are two real-world examples:
Woodside Energy created a virtual plant where trainees wearing VR headsets can walk through the environment, hear what everything sounds like, and understand how everything works before going on site.
One global consumer goods company created a company-wide digital academy, upskilled more than 2,000 employees, and achieved a 15% productivity boost worth tens of millions in savings—while also strengthening workplace safety.
Virtual manufacturing environments show just how precise and intuitive this training can be—see the video below to understand how it works.
6. Business-aligned sustainability
Here's how digital transformation tackles sustainability challenges head-on:
IIoT sensors show how equipment is running and where resources are wasted. With that data, you can cut energy use, reduce scrap, and improve material flow.
AI analytics identifies patterns across the supply chain, making it easier to choose greener options without slowing production.
Digital twins create a lasting record of your facilities. That record supports energy-efficient upgrades, simplifies sustainability audits, and enables remote visual inspections that reduce travel-related emissions.
Whether you're dealing with regulations or chasing environmental goals, these technologies deliver measurable results—fast.
Common challenges of scaling digital transformation in manufacturing
Many manufacturers struggle with digital transformation because they haven’t considered all the factors involved in adopting the new, while the old is still in operation.
Here's what these issues are about and how to solve them:
Disconnected systems
Most manufacturing facilities have a patchwork of systems that connect haphazardly. CMMS, EAM, and SCADA platforms often run side by side without sharing data, duplicating work and creating operational blind spots.
When systems don't communicate, you waste time stitching data together instead of acting on it.
How to address it: The way forward is interoperability. APIs, SDKs, and standardized data models can help unify fragmented systems. Middleware and open protocols go a step further, ensuring your tech stack stays flexible as new tools are added.
Low tech adoption
Poor adoption not only delays ROI but also creates safety risks when workers don’t feel confident with new systems. It also increases frustration and turnover when skilled labor is already scarce.
How to address it: Blend modern training methods with the reality of factory life. Immersive simulations, AR/VR onboarding, peer coaching, and accessible e-learning help employees build confidence quickly while minimizing downtime.

Use the principles of change management whenever introducing new technologies and processes. (Source)
Unscalable pilots
“Pilot purgatory” is one of the most common reasons digital transformation loses momentum. Manufacturers often run successful pilots at one site, only to see them stall before enterprise-wide rollout.
What happens without clear KPIs and buy-in? Pilot results get stuck in silos and everyone loses steam.
How to address it: Set standards early. Align stakeholders around enterprise-wide goals, establish a governance model, and make sure executive sponsorship is strong enough to carry projects from one facility to many.
How Siemens used digital twins to innovate their manufacturing operations
Siemens accelerated digital transformation in their facilities globally by applying Matterport digital twins across multiple use cases:
Remote collaboration: Captured 4,000 m² of a manufacturing plant in Asia, enabling virtual reviews of shop floor and warehouse layouts without disrupting production.
Training and onboarding: Digitized nearly 30,000 m² of its Lisbon corporate campus, simplifying navigation for new employees and visitors while enabling virtual tours.
IoT integration: Linked digital twins with real-time sensor data at the Siemens Experience Center, providing spatial context for IIoT applications and smarter monitoring.
Factory relocation: Used digital twins in Berlin to virtually stage equipment, confirm spatial fit with 99% accuracy, and reduce costly rework. Sales and marketing: Created a virtual tour of a 1,700 m² E-House in Brazil, enabling customers to explore complex systems remotely and accelerating purchasing decisions. Explore the E-House below by clicking on the image.
These digital transformation examples in manufacturing demonstrate how companies can achieve measurable ROI through strategic technology adoption. Now, Siemens enjoys greater manufacturing flexibility, stronger knowledge sharing, and measurable savings across both operations and sales.
How to adapt to the future of digital transformation in manufacturing
Not sure where to start? These three strategic shifts will set your facility up for long-term success.
First, think in ecosystems, not individual tools. The future of manufacturing relies on interconnected systems that share data seamlessly. Evaluate whether new technology integrates with existing tools and supports emerging standards like IoT and cloud connectivity.
A Matterport digital twin integrated with AWS IoT TwinMaker is a great example of an integrated system. It connects your physical facility data with cloud analytics, letting you test production scenarios virtually while tracking real-time equipment performance, all on one dashboard.
Second, prep for distributed operations. Technology must support remote collaboration and monitoring. Centralizing facility data in accessible digital formats enables remote work and reduces on-site requirements.
Third, build infrastructure that scales easily. Your current workforce needs upskilling, and new hires need faster onboarding. Augmented reality (AR) reduces the time from hire to productivity while improving safety outcomes. Simulating high-risk scenarios and complex operations in digital environments builds lasting institutional knowledge.
